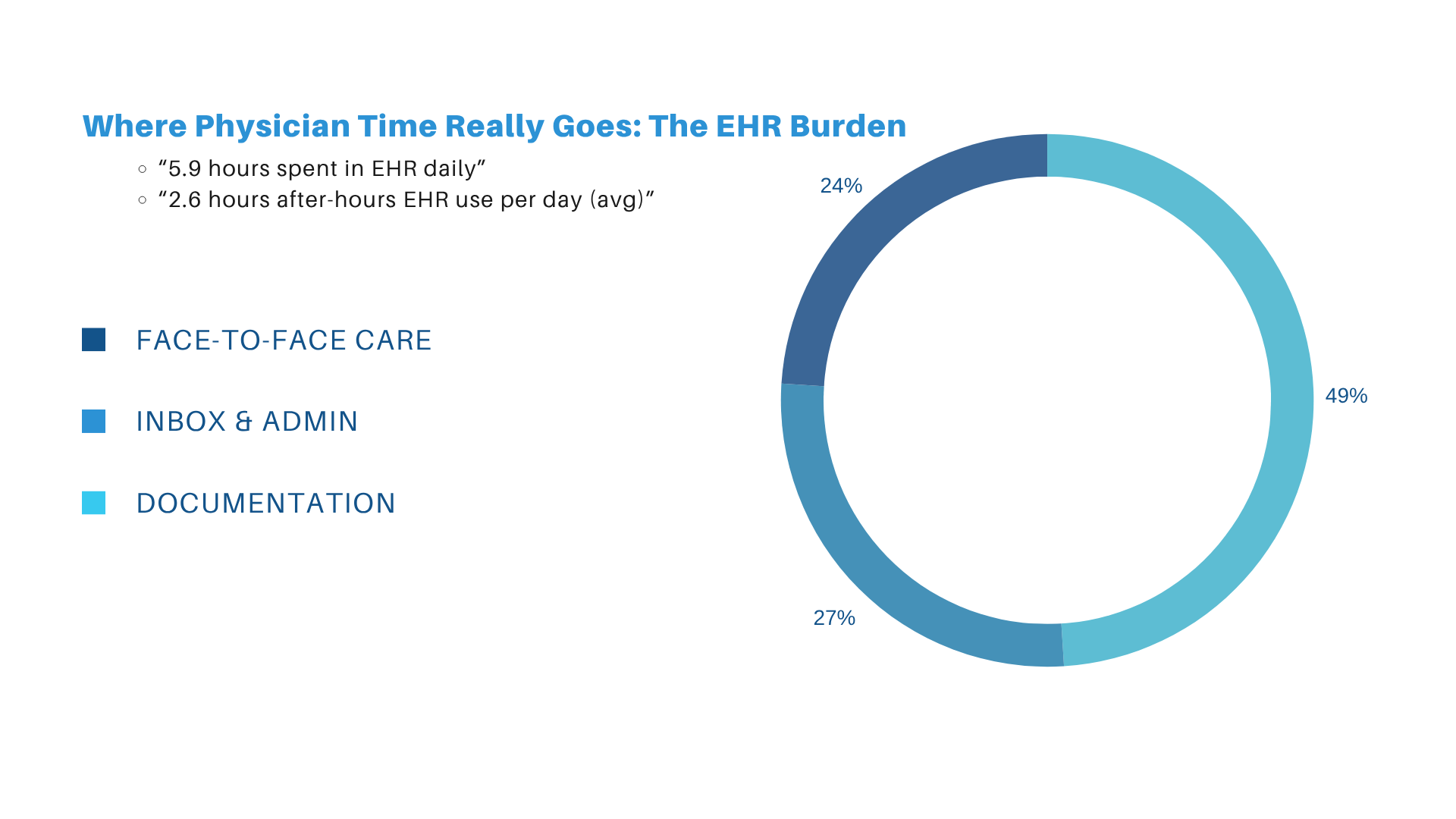
For the past decade, electronic health records promised efficiency, accuracy, and “more time for patients.” Instead, EHRs became one of the top drivers of burnout in modern medicine. A major study in Annals of Family Medicine found that primary care physicians now spend nearly two hours on EHR tasks for every one hour of direct patient care. Another time-motion analysis showed physicians click the mouse over 4,000 times per shift in some specialties.
This imbalance—more screen time than patient time—isn’t just frustrating. It’s clinically dangerous. Documentation fatigue contributes to diagnostic errors, delayed notes, incomplete coding, and after-hours work (“pajama time”), which now affects over 70% of outpatient physicians.
Amid this worsening trend, a new class of tool has emerged inside modern EHRs: the AI medical assistant. Unlike traditional dictation or macros, these systems understand clinical context, structure data automatically, and work passively in the background as physicians speak, type, and examine patients.
MedTec’s AI assistant is a representative example of this new generation of tools. When used well, it fundamentally changes how primary care physicians, specialists, and multi-site groups operate.
What an AI Medical Assistant Actually Is (and What It’s Not)
Most clinicians have used speech-to-text dictation or templated macros.
An AI medical assistant is not either of those.
Instead, MedTec’s system functions as a real-time clinical intelligence layer embedded within the EHR.
It performs four categories of tasks:
-
Ambient clinical capture
The assistant “listens” (with permission) to the clinical conversation—both patient and provider contribution—and extracts key data:
-
Symptoms
-
Duration/timing
-
Medications
-
Relevant history
-
Physical exam findings
-
Risk factors
-
Red flags
It doesn’t just transcribe—it interprets.
-
Real-time documentation synthesis
Instead of waiting until the visit is over, the system generates structured:
-
HPI
-
ROS
-
Physical Exam
-
Assessment & Plan
-
Orders, referrals, labs, follow-ups
It uses medical ontologies such as ICD-10, CPT, SNOMED-CT, and LOINC to organize data into EHR-ready fields.
-
Clinical suggestion engine
The system can flag:
-
Missing components (“No neurological exam documented for limb numbness”)
-
Potential diagnoses
-
Potential CPT/E&M levels
-
Care gaps
-
Medication adherence issues
-
Risk stratification (ASCVD, GAD-7 trends, etc.)
-
Workflow automation
The assistant can propose:
-
Follow-up intervals
-
Patient instructions
-
Referrals
-
Billing codes
-
Prior authorization support
-
Evidence-based guidelines
It does NOT make diagnoses independently. The clinician remains in full control.
The Real Problem: Documentation Isn’t Just Annoying; it’s a Clinical, Financial, and Safety Risk
-
Cognitive overload and clinical accuracy
Numerous studies show that physicians performing high volumes of clerical work experience narrowed diagnostic focus and reduced recall. EHR multitasking increases the rate of:
-
Missed abnormal labs
-
Incomplete documentation
-
Inaccurate medication reconciliation
-
Diagnostic anchoring
The AI assistant acts as a “second set of eyes,” reducing the cognitive burden of remembering every detail while examining the patient.
-
Documentation gaps lead to coding errors
Under-coding and over-coding cost practices hundreds of thousands annually.
Common problems include:
-
Missing exam elements
-
Missing chronic condition documentation
-
Incorrect time capture for time-based billing
-
Incomplete MDM justification
MedTec’s AI assistant automatically identifies missing required elements for E&M levels and suggests potential codes based on documented complexity.
-
After-hours documentation is harming clinicians
AMA studies show:
-
63% of physicians spend more than one hour every day finishing charts at home
-
“Pajama time” is linked to burnout, depression, and early job turnover
-
Charting outside the encounter increases documentation error rate
AI assistants significantly reduce after-hours workload by completing notes in real time.
How AI Medical Assistants Change Daily Workflow (Practically, Not Theoretically)
Primary Care Example
A PCP seeing 20–25 patients daily typically finishes 1–2 hours behind. With an AI assistant:
-
The note is generated while you’re talking with the patient
-
Care gaps (mammogram, A1c, vaccines) appear automatically
-
Medication history is summarized intelligently
-
E&M level suggestions appear instantly
-
Follow-up instructions are generated based on guidelines
PCPs often report saving 40–90 minutes per day.
Specialists
Specialists often require detailed procedural, diagnostic, or longitudinal documentation.
Example scenarios:
-
Cardiology: Automated extraction of chest pain descriptors, NYHA class, functional status
-
Orthopedics: Injury mechanism, laterality, range-of-motion values
-
Neurology: Seizure frequency, focal deficits, timeline qualifiers
-
Psychiatry: PHQ-9, GAD-7, medication adherence, risk assessments
The AI assistant identifies missing specialty-specific elements and builds structured, detailed notes that reduce audits and improve clinical clarity.
Small Private Practices
These practices often lack scribes and have limited admin support.
AI assistants:
-
Reduce staffing dependency
-
Improve revenue consistency
-
Shorten charting time dramatically
-
Standardize documentation across providers
Multi-site Groups / MSOs
Enterprise groups face a different problem: variation.
AI assistants reduce variability in:
-
Documentation quality
-
Coding accuracy
-
Guideline adherence
-
Operational throughput
Large practices using AI assistants often see a 10–15% increase in coding capture due to reduced under-coding.
Scientific Evidence Supporting AI-Driven Documentation
The shift toward ambient clinical intelligence isn’t anecdotal. It’s data-driven.
-
Time Savings
Studies of AI medical scribes show:
-
30–70% reduction in documentation time
-
2–3 fewer hours of charting per day
-
40% reduction in after-hours work
MedTec’s user reports align with this range.
-
Accuracy and completeness
AI-generated notes have been shown to:
-
Reduce incomplete documentation by 25–45%
-
Improve coding accuracy by 15–20%
-
Reduce manual transcription errors
-
Increase capture of chronic conditions (important for risk score models)
-
Burnout reduction
When physicians offload clerical tasks to AI, surveys show improvements in:
-
Emotional exhaustion
-
Job satisfaction
-
Work-life balance
-
Cognitive clarity during visits
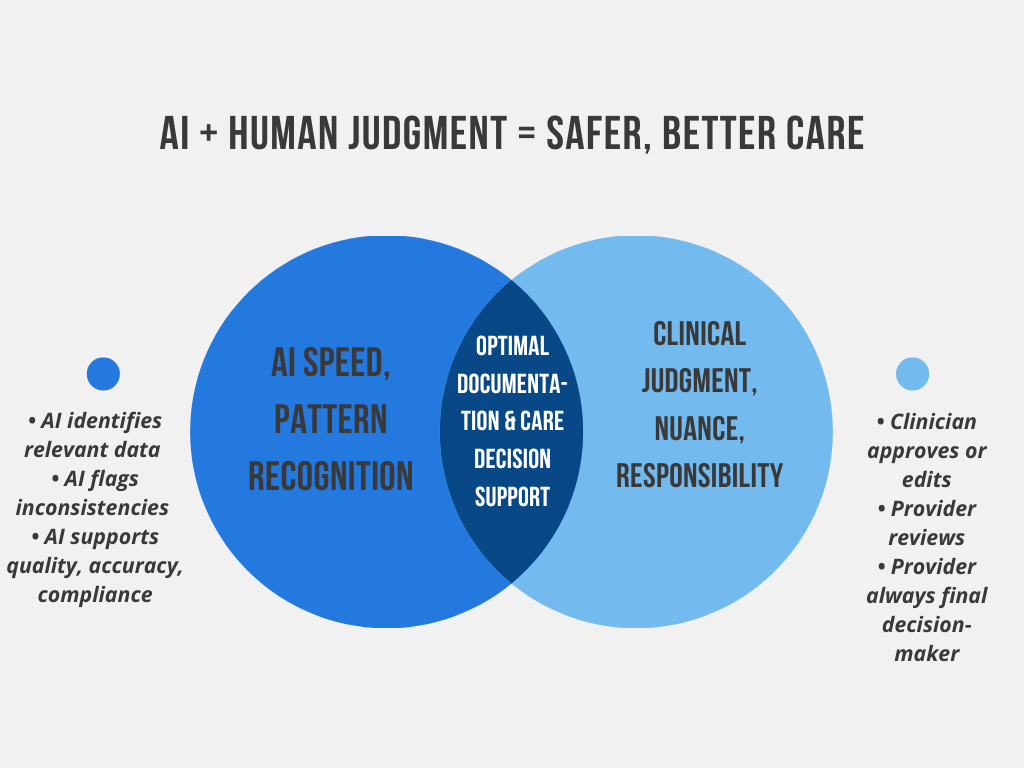
AI + Human Judgment: Why the Combination Works
AI is not replacing physicians for three fundamental reasons:
-
Medicine requires nuance
Patients describe symptoms vaguely. AI helps structure, but interpretation remains human.
-
Clinical reasoning is context-dependent
Algorithms support thinking—physicians perform the reasoning.
-
Accountability and autonomy must remain with the clinician
MedTec ensures all AI-generated suggestions are editable, reviewable, and transparent.
The best model is a partnership:
AI handles the clerical work. Physicians handle the clinical work.
Risk Mitigation, Compliance, and Audit Protection
AI assistants strengthen compliance by:
-
Ensuring notes contain all required elements
-
Flagging contradictory statements
-
Suggesting additional documentation for complex visits
-
Improving MDM clarity
-
Supporting proper E&M leveling
For multi-site groups, this dramatically simplifies audit preparation.
The Future: Predictive, Personalized, Fully Integrated Clinical Workflows
Within the next 2–4 years, AI medical assistants will evolve to:
-
Predict the next likely order or diagnosis
-
Recommend guideline-based care plans
-
Identify patient-specific risks
-
Auto-fill chronic condition updates
-
Assist in population health and value-based care analytics
Practices that adopt AI assistants early will transition smoothly.
Those that don’t may struggle as documentation requirements continue to intensify.



